A robust approach to cybersecurity exists, and it’s called zero trust security. Let’s look at how it works and who should implement it.
Table of Contents
Why Robust Security is Vital
The days of employees working from a single location with support from local IT infrastructure are long gone. Remote work has become not only common but also highly desirable. With this shift, the traditional network perimeter has vanished. Employees now use a mix of work and personal devices to access an expanding array of cloud services, redefining the modern workplace.
This new IT environment has made traditional approaches to cybersecurity ineffective. Thus, leading to an explosion of data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other costly incidents. Fortunately, businesses can leverage zero trust security to enhance their cybersecurity and protect themselves from these threats.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
As the name implies, zero trust security is a security model that doesn’t trust any user, device, or application by default, regardless of whether they’re located within the main network or outside.
Don’t be surprised if this model seems familiar to you. It was actually first presented by an analyst at Forrester Research Inc. in 2010.
While many large enterprises have been relying on it for a long time, most SMBs were perfectly content with the castle-and-moat approach to security.
Castle-and-Moat Approach
In the castle-and-moat approach, everything inside the network (the castle) is trusted, and only outside connections are verified by a firewall or other security tools (the moat).
However, this model breaks down when employees must work outside the office – whether that’s due to something like a global pandemic or because organizations adopt cloud technologies to boost efficiency and reduce costs.
As soon as an intruder gets over the moat, they can do whatever they please inside the castle. That’s unacceptable!
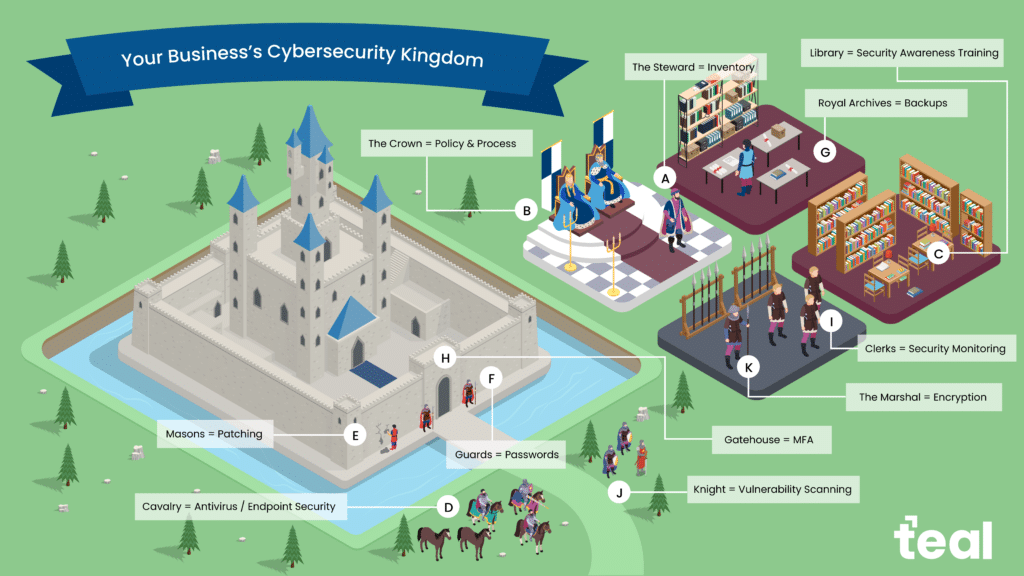
Zero trust security takes a proactive approach by always authenticating and authorizing all users, devices, and applications—even those already inside the “castle.”
This ensures that no entity is automatically trusted, reducing the risk of a single intrusion leading to disastrous consequences.
Essentially, it ensures that every door inside the castle is safely locked at all times and impossible to open by force.
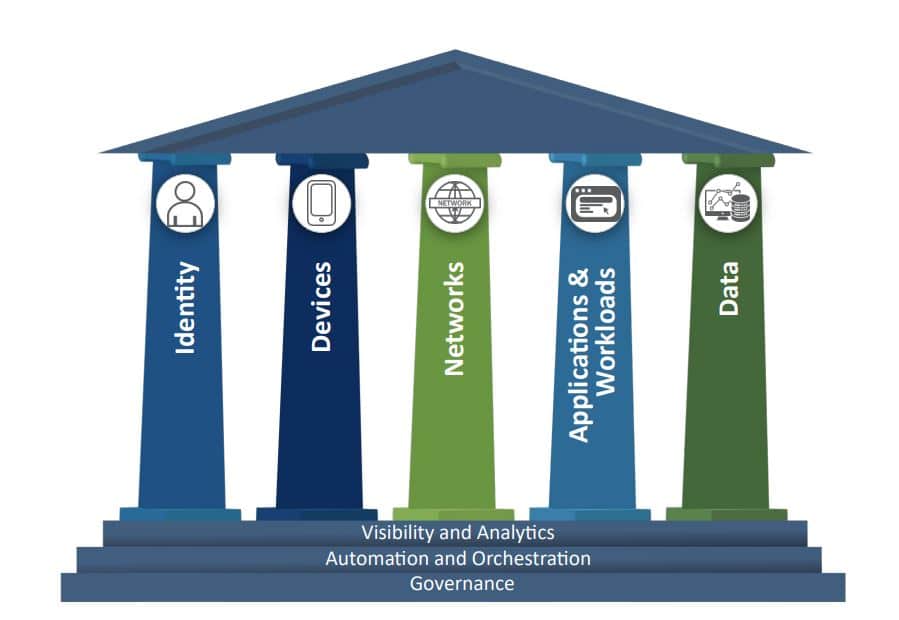
When a remote employee working for an organization that has adopted the zero trust security model becomes compromised, the impact is highly localized because the threat is unable to move laterally across the network and keep spreading.
The same happens when a third-party cloud vendor becomes infected with malware, or when one employee’s personal mobile device has spyware installed on it.
What Are the Main Benefits?
According to a recently published report, the global market size of zero trust security is expected to reach $51.6 billion by 2026 from $19.6 billion in 2020, growing at a CAGR of 17.4 percent.
Clearly, many organizations see it as the best way forward. However, improved security posture isn’t the only benefit they’re attracted by.
Here are three other important benefits that you should know about.
1. Enhanced Compliance
Zero trust security relies heavily on microsegmentation, the creation of many small perimeters. This makes it possible for organizations to control exactly how, when, and by who certain types of data are accessed. Such a granular level of access control is a boon when it comes to supporting compliance initiatives.
2. Accelerated Digital Transformation
Security is one of the biggest obstacles organizations need to overcome when they decide to embrace digital transformation. Zero trust security provides a holistic solution for addressing the challenges associated with moving from analog to digital, regardless of what the move involves.
3. Improved Network Visibility
Because zero trust security assumes that all connections are potentially malicious, it requires real-time monitoring of the entire network to vet connections coming from both inside and outside the local network. As a result, organizations get to enjoy a comprehensive record of all network activity. This allows them to check every access request and see exactly who and when made it.
How to Achieve Zero Trust Security?
Zero trust security is a holistic security model, so it doesn’t depend on any specific technology.
There are, however, certain principles that all zero trust security implementations must follow:
- Explicit Verification: Always authenticate and authorize regardless of where the access request comes from.
- Least Privileged Access: Let trusted users, devices, and applications do only what they’re trusted for.
- Microsegmentation: Divide the network into microsegments to prevent malware from moving laterally across it.
Since there are countless different ways to achieve zero trust security, it’s paramount that you select the approach that best meets your needs and requirements.
At Teal, we deploy advanced tools to empower organizations with capabilities like application whitelisting, ringfencing, and data storage control. These solutions provide everything needed to continuously monitor user behavior and authenticate every request.
Our approach is cost-effective and adaptable for organizations of all sizes. Get in touch with us to learn how we can help you achieve complete control over your endpoints.














