Ransomware is no longer a distant threat. With attacks growing in sophistication and cost, every business is a prime target. Making it an existential risk to small and mid-market organizations.
From encrypting critical files to halting operations for days or weeks, ransomware attacks are increasingly targeting sectors like healthcare, construction, finance, manufacturing, nonprofits, and government contractors.
Want to get ahead of the threat?
Download our in-depth research guide, complete with a strategic prevention checklist and executive-level guidance to help you assess and strengthen your ransomware defenses.
Small businesses are being hit harder than ever by ransomware attacks. This guide gives you a clear, actionable strategy to reduce risk and improve cyber resilience.
Table of Contents
Ransomware: An Existential Threat
When your operations are halted by ransomware, you’re faced with a difficult decision: pay the ransom and hope the cybercriminals restore access to your data or attempt to restore access yourselves.
Either way, your business’s survival is on the line and will benefit from all the ransomware tips you can get your hands on.
The average recovery cost from ransomware is now $2.73 million, with over a month of downtime.
Source: State of Ransomware, Sophos
Common Attack Vectors
Attackers often leverage phishing emails to trick their victims into clicking on an attachment, which runs malicious software that takes over their computer.
Malware
Cybercriminals quietly plant malicious code through security gaps in a victim’s network or software. This attack may remain unnoticed at first, giving attackers time to steal data or move laterally through their systems.
Other Examples of How Ransomware Can Occur
1. A user is tricked into clicking on a link in a phishing email – which downloads a malicious file from an external website.
2. Ransomware simultaneously encrypts all the victim’s files, then displays a message demanding payment in exchange for decrypting them.
Brief History of Ransomware
The AIDS Trojan, also known as the PC Cyborg virus, was the first recorded ransomware virus. It was distributed, via floppy disk, in 1989 at the World Health Organization’s AIDS conference – long before most of us had access to a personal computer.

Ransomware message displayed from the 1989 floppy disk.
By the 2020s, cybercriminals were wreaking havoc with ransomware – making national headlines with high-profile attacks like Colonial Pipeline, WannaCry, and SolarWinds.
Verizon’s 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report revealed that ransomware attacks rose nearly 13% – equal to the combined increase of the previous five years – and were involved in almost 70% of all malware-related breaches.
This made it absolutely clear that ransomware is no longer a fringe threat. It was a threat that every person and organization needed to acknowledge.
Small Business Ransomware Risk & Brand Impact
Data, Data & Even More Data
The risks associated with ransomware continue to grow. Not just because attacks are growing more prolific, but because data volumes are expanding at an exponential rate with no sign of slowing down.
IDC projects that by 2026, businesses will be storing 12.8 zettabytes of data. To put that in perspective, you’d need over 154 million years to watch that much content in 720p HD.
Many experts recommend a cloud-first approach to boost data resilience; however, it’s important to note that the cloud is still vulnerable to ransomware attacks.
67% of businesses lost sales because ransomware shook customer confidence in their security.
Above the Clouds, Security Dangers Lurk
In 2023, Blackpoint Cyber reported that 90% of cyberattacks targeted cloud environments. Additionally, they found that ransomware attacks using double extortion tactics (data theft + encryption) surged by 64%, and 75% of human-operated ransomware incidents involved compromised privileged accounts.
With ransomware attacks increasingly targeting cloud environments and exploiting compromised credentials, businesses can’t afford to rely on basic defenses. That’s why more businesses are turning to Managed Detection and Response (MDR).
It provides 24/7 monitoring, rapid threat containment, and expert responses – which is great for businesses that fall under compliance regulations. It closes the gaps that traditional tools, like SIEM, often miss and significantly reduces cloud security risks.
When Regulators Get Serious, So Should Your Strategy
Regulators are catching up to the ransomware threat, meaning compliance today requires a whole lot more than firewalls and paper policies.
In 2023, the SEC began requiring timely disclosure of cyber incidents, and more states are mandating formal risk assessments. Frameworks like NIST CSF and the 2024 CMMC updates are setting clear expectations for how businesses should prepare and respond.
Implementing Zero Trust principles can streamline compliance by limiting access, enforcing authentication, and generating detailed audit trails.
This proactive approach not only satisfies regulatory demands for your business, but it also reduces ransomware attack risks and reassures stakeholders that their data is in trusted hands.
Don’t Let Third Parties Be Your Blind Spot
Today’s businesses rely on a complex web of vendors, platforms, and partners. However, each connection creates another potential entry point for ransomware.
Attackers know that smaller suppliers often have weaker security – which makes them the perfect backdoor into larger networks. In fact, many high-profile breaches in recent years started with a compromised third party – such as the AT&T Snowflake data breach.
Managing supply chain risk means going beyond trust…it requires verification. That includes vetting vendors for security practices, limiting their access to only what’s necessary, and regularly reviewing who has access to your data and systems.
If your partners don’t take cybersecurity seriously, they could become your biggest liability.

Security Isn’t Optional When Consumer Trust Is on The Line
The study Privacy Front & Center, conducted by Consumer Reports’ Digital Lab and Omidyar Network, found that 96% of Americans believe “companies should do more to protect consumer privacy.”
When businesses fail to take cybersecurity seriously, customers often take their trust – and their business – elsewhere. And Cisco has data to back that up.
It’s rarely wise to pay ransomware demands.
There’s no guarantee of data recovery, and payment often invites future attacks.
According to the 2023 Data Privacy Benchmark Study, 94% of organizations said customers would stop buying from them if their data weren’t properly protected. Reputation damage and customer trust erosion can be more costly than the ransom itself.
The Takeaway
Ransomware isn’t going away, and neither is the amount of data businesses handle. Moving to a cloud-first approach makes sense for flexibility and resilience.
However, it doesn’t mean that you’re off the hook when it comes to security because attackers go where the business is, and that includes yours.
In 2022, 24% of businesses were hit by ransomware once.
45% suffered multiple encryption attacks.
Additionally, if your customers sense that their information isn’t safe, they won’t hesitate to take their business to competitors who’ve made cybersecurity a priority.

A Typical Ransomware Attack Workflow
Ransomware attacks on businesses are rarely impulsive. They’re methodical, multi-phase operations designed to maximize damage and payout. Understanding the typical workflow can help you better anticipate and defend against them.
How Ransomware Attacks Work
1. Initial Access via Trojan or Phishing
The attack usually begins when a user unknowingly downloads a “stager.” This is a trojan horse disguised as a legitimate file or link. This lightweight program quietly modifies the host system and establishes a foothold.
2. Downloading Tools and Payloads
The stager then connects to a command-and-control server to download updates, malicious payloads, and instructions – which are all tailored to bypass detection.
3. Reconnaissance
Once inside, the malware collects as many passwords and credentials as possible. Hackers use this data to escalate privileges and move laterally across your network.
4. Evasion and Persistence
The malware continuously updates itself to stay ahead of endpoint detection and response tools and antivirus software. New payloads may be deployed, and the infection spreads quietly to other devices.
Avoiding Detection
Without strong detection and response measures, SMBs may not realize they’ve been breached by ransomware until it’s too late.
Dwell time (the period between initial access and attack) can range from days to up to 8-12 months. This gives attackers ample time to steal, study, and strategize.
5. Manual Targeting
Once a foothold is secure, the attacker may log in manually to analyze your systems, find valuable data, and assess your ability to recover.
6. Exfiltration and Theft
Before launching encryption, attackers often steal sensitive data, like financial records, intellectual property, employee info, and customer data. This tactic is a more aggressive strategy known as double extortion.
7. Encryption and Ransom Demand
Finally, encryption is deployed to lock down systems and data. A ransom note follows, demanding payment in exchange for a decryption key, often threatening further consequences if you don’t comply.
The Harsh Reality of Double Extortion
In modern ransomware attacks, backups alone won’t protect your business from the consequences.
While you may have backups you can restore your systems with, attackers may use double extortion to:
- Leak stolen intellectual property or data publicly or on the dark web.
- Threaten employees or customers directly if you don’t pay the ransom.
- Publicly shame your company to pressure you into paying them.
- Report your breach to regulators before you can.
A Word of Caution for the Healthcare Industry
Attacks on hospitals, pharmacies, and healthcare providers is a patient safety crisis. The liability is massive, but the cost is human.
One missed alert, a wrong dosage, or a delayed procedure can lead to injury or even death.
In these moments, your business isn’t just facing data loss from a ransomware attack. You’re facing legal damages, regulatory penalties for noncompliance, public trust erosion, and the irreversible consequences of downtime.
Every leader needs to ask: If a ransomware attack hits tomorrow, are we really prepared to protect our patients, our people, and our reputation?

The Insurance Safety Net. Or Is It…?
Having cyber insurance reassures customers, partners, suppliers, and employees of an organization’s preparedness for averting or withstanding a cyberattack.
However, it’s not the safety net for your business that it once was – especially when it comes to ransomware attacks. As attacks grow more frequent and costly, insurers are tightening the rules.
Many policies now come with strict conditions, reduced coverage, or even outright exclusions for ransomware-related incidents.
That means businesses can no longer rely on insurance alone to mitigate the financial fallout of an attack. Leaders need to prioritize prevention and resilience to mitigate the toll advanced cyberattacks have on their organization.
Challenges with Ransomware Insurance
Strict qualification requirements: Organizations with past ransomware claims may find that they cannot get – or renew – insurance without improving their defenses.
Policy considerations or exclusions: Many policies have ransomware exclusions or conditions (e.g. whether a ransom payment is covered). Opting out of these coverages might lower your policy premium, but it also significantly reduces your financial protection in the event of a ransomware attack.
What Cyber Insurance Typically Covers
- Business interruption
- Legal fees
- Data loss or damage
- Data restoration
- Ransom demands
- Public relations
- Forensic analysis
- Client notification
- Regulatory notification
- Credit monitoring
Frequent Triggers of Cyber Insurance Claims
- Ransomware
- Business email compromise
- Hacking
- Monetary theft
- Employee errors
Source: NetDiligence Cyber Claims Study 2023
Zero Trust, Zero Assumptions: A Smart Security Strategy
Leveraging the Zero Trust security model can significantly reduce the risks of ransomware attacks for small and mid-sized businesses. Unlike traditional security approaches that assume internal networks are safe, Zero Trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
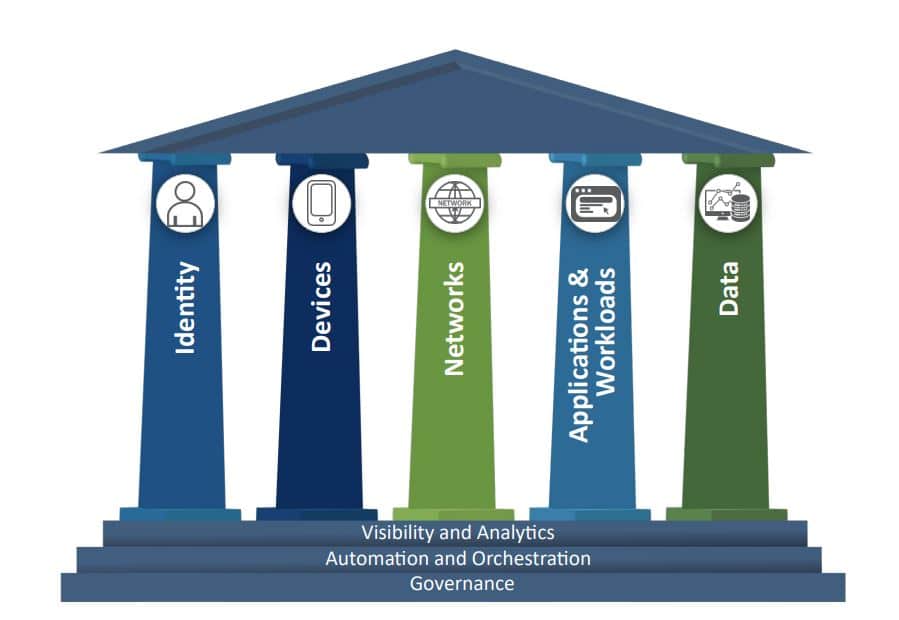
This means that every user, device, and application must be continuously validated, regardless of their location within or outside the network
The model’s emphasis on strict access controls and continuous monitoring helps prevent unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network. This containment strategy is exceptional in limiting the spread of ransomware attacks in your business.
Remember, Backups Won’t Save You
Backups are a critical part of your cybersecurity strategy, but they’re not a silver bullet. A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is what truly protects your business, and IT professionals must make that clear to their leadership team because…
The threat isn’t the ransomware itself. It’s how attackers got in.
By the time the encryption begins, the real damage has already been done. So, it’s vital your company’s leadership understands that ransomware resilience requires layered defense, constant vigilance, and executive support to succeed.
Don’t wait until ransomware locks you out.
Stop ransomware attacks with our MSP’s expert guide – complete with prevention strategies and a proven incident response checklist.

Small businesses are being hit harder than ever by ransomware attacks. This guide gives you a clear, actionable strategy to reduce risk and improve cyber resilience.
How a Managed IT Service Provider Builds Your Resilience
Your cybersecurity goal isn’t to eliminate all threats. That’s impossible.
Instead, your objective should be to make your company a harder target than the next. That’s where a managed IT service provider (MSP) plays a critical role.
Partnering with a reputable MSP is one of the most effective, cost-efficient ways to build cyber resilience in your business against threats like ransomware attacks.
They bring to bear enterprise-grade expertise, tools, and vigilance to businesses that don’t have the in-house resources to keep up with fast-evolving cyber threats.

Optimizing your IT investment starts here. Explore our MSP pricing guide to understand costs, factors, and models.
Services to Look for in a Reputable MSP
A qualified MSP will build your resilience by implementing a layered, proactive defense strategy.
Employee Security Training
Most successful cyberattacks exploit human error. An MSP will provide ongoing training to all employees – from onboarding to monthly updates – to help them recognize phishing attempts, suspicious behavior, and risky habits.
Simulated Phishing Campaigns
A strategic MSP partner will ensure the effectiveness of your security training by regularly deploying simulated phishing campaigns to test your staff’s knowledge retention – which will give you measurable insights into your team’s readiness.
Password Management
Using enterprise-grade password management tools (like LastPass or 1Password), your MSP can help employees create and store complex, unique passwords – which reduces the risk of credential-based attacks.
Firewall Management
This includes installing, updating, and actively monitoring firewalls to prevent unauthorized access and contain breaches before they spread.
Antispam & Antivirus Tools
Your MSP ensures your systems are protected with the latest anti-malware solutions and continually tests them to confirm they’re working effectively.
Device & Communication Encryption
Encryption ensures sensitive data on your computers, mobile devices, and emails stays protected – even if devices are lost or stolen.
Patch Management
Cybercriminals exploit outdated software. MSPs take the burden off your team by promptly applying security patches and software updates across all systems.
Security Policies & Procedures
A strong MSP will help you document cybersecurity policies tailored to your business and industry regulations. These documents ensure staff know what’s expected and provide a basis for legal compliance and liability protection.
Data Backup & Disaster Recovery
MSPs provide regular, secure backups with clearly defined recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). This ensures minimal downtime and data loss in the event of a ransomware attack or other disaster.
Dark Web Monitoring
This service scans black-market forums for stolen company credentials, giving you early warning of compromised accounts and helping refine your security training and response.
Why It Matters for Your Business
A cybersecurity breach can cost your business tens – or hundreds – of thousands of dollars, and the damage to your reputation can take months or even years to repair.
According to a Nationwide Insurance study, over 20% of SMBs spent more than $50,000 after a cyberattack.
Some paid over $100,000 and needed a year or more to regain customer trust.
The Strategic Advantage of Partnering with an MSP
Here’s where an MSP goes beyond basic tech support to become a strategic security partner.
Regulatory Compliance
If your business operates in a regulated industry, an MSP with credentials like CompTIA Security Trustmark+, ISO 27001, or strong third-party ratings (e.g., SecurityScorecard) can help you build and maintain a compliant cybersecurity framework.
Example
A financial services firm subject to SEC/FINRA oversight or a government contractor working under CMMC requirements can rely on a qualified MSP to prepare for audits, manage evidence, and reduce compliance risk.
Legal Liability Protection
In the event of a breach, your MSP’s documentation and oversight may serve as evidence that your company took “reasonable measures” to protect customer data – an important factor if legal action is taken.

Strategic Partner, Strategic Oversight
Teal is a sophisticated managed IT services provider that will guide your technology decisions through a long-term business lens, including cybersecurity.
We’ll help you combat ransomware with dedicated, compliance-ready cybersecurity that’s built into our managed IT services.
Here’s how our sophisticated services help you sleep better at night:
- Predictable IT spending
- Avoid the skyrocketing costs of a breach
- Business continuity through proactive monitoring and rapid recovery
- Peace of mind with 24/7 expert oversight
- Specialized cybersecurity expertise without the hiring overhead
- Enterprise-grade tools and threat intelligence that go beyond in-house capabilities
- Scalable support aligned with your growth
- Strategic consulting
We’re not just another MSP. We’re your strategic IT and security partner and our credentials speak for themselves:
We offer responsive and secure managed IT services to SMBs nationally, with local business IT solutions provided in:
Speak with a Teal business technology advisor today to discuss your IT and security challenges.













